close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-09 Origin: Site
Optical mirror coatings help mirrors reflect light better and stay strong. Scientists and engineers use these coatings for many things. People use them in telescopes, microscopes, and laser systems. Some mirrors show images, bend light, or spread beams. Other mirrors help with security, astronomy, or life sciences. There are three main types: metallic, dielectric, and hybrid coatings. Each type has special benefits for different jobs.
Optical mirror coatings help mirrors reflect more light. They also protect mirrors from getting damaged. This makes images look clearer. It also helps mirrors last longer.
There are three main coating types: metallic, dielectric, and hybrid. Each type has its own good points. This makes them work well for different uses.
Metallic coatings like aluminum and silver cost less. But they may not last long in tough places. Gold coatings last longer but cost more money.
Dielectric coatings reflect more light at certain angles and colors. This makes them great for lasers and tools that need precision. They also last longer than metallic coatings.
When picking a coating, think about how you will use the mirror. Also think about the environment and your budget. Anti-reflective layers can make mirrors work better and make images clearer.

Image Source: unsplash
Optical coatings are very important in science and technology. They help mirrors reflect more light and make pictures look better. If a mirror does not have a coating, it can lose a lot of light. This makes the image look worse. Coatings also keep mirrors safe from scratches and damage. This helps mirrors last longer. Engineers make coatings with special layers. These layers control how light acts. They can change how much light goes through or bounces off the mirror. People can pick coatings that give more protection or better reflection.
Optical coatings do more than just help with reflection. They also make mirrors stronger and help them last longer.
Optical coatings help light move and bounce better, so systems work well.
Coatings have many layers to make special effects with light.
They make mirrors harder and stronger.
Mirrors without coatings can lose light and make images look bad.
Coatings can be made for different jobs.
There are three main types of optical mirror coatings. Each type has good and bad points.
Metallic coatings use metals like aluminum, silver, or gold. These coatings reflect light well and are used in many tools.
Dielectric coatings use thin layers of special stuff. These coatings can reflect almost all light at some wavelengths and are hard to damage.
Hybrid coatings mix metallic and dielectric layers. They give strong reflection and more protection.
Each type helps mirrors work in different ways. Scientists and engineers choose the best coating for their project.

Image Source: unsplash
Metallic coatings are important in many optical systems. These coatings use metals like aluminum, silver, and gold. They help mirrors reflect light better. Each metal has its own special features.
Aluminum coatings are found in many mirrors and science tools. People pick aluminum because it is cheap and works for most uses. Aluminum reflects a lot of visible and near-infrared light. Engineers use it in telescopes and solar tools.
Aluminum coatings last long and keep reflecting well.
They work in regular mirrors and stage lights.
Aluminum does not reflect as well as silver or last as long in harsh places.
Aluminum coatings can resist some corrosion. They usually last 12 to 24 months in labs or outside.
Silver coatings reflect the most visible light of all metals. Many optical systems use silver for bright, clear images. Silver can reflect up to 95% of visible light. This makes it good for high-quality mirrors.
| Evidence Description | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur and moisture in air | Silver can rust and break down | Air quality changes how long it lasts |
| Enhanced dielectric Ag coatings | Sticks well and resists sulfur | Lasts longer |
| Silver oxide formation | Silver reacts with water and forms oxides | Oxides make it reflect less |
| Reaction with H2S | Silver sulfide makes it look dull | Dullness lowers performance |
| Long-term storage | Better coatings stay strong over time | Works better for longer |
Silver needs protection from air and water. If not protected, it can get dull and lose shine. Special coatings help silver last longer and keep working well. Silver coatings last about 12 to 24 months, like aluminum.
Gold coatings are great for reflecting infrared light. Gold does not get dull easily, so it works in tough places. Scientists use gold in infrared detectors, thermal cameras, and space telescopes.
| Coating Type | Wavelength Range (nm) | Average Reflectivity (Ravg) |
|---|---|---|
| Protected Gold | 700-2000 | >96% |
| 2000-10000 | >96% | |
| Bare Gold | 700-800 | >94% |
| 800-20000 | >97% | |
| 2000-12000 | >98% |
Gold reflects infrared light very well. It resists rust better than aluminum and silver. Gold costs more, so people use it only for special needs.
Metal mirror coatings have good and bad sides. The table below shows the main pros and cons.
| Advantages of Metallic Mirrors | Disadvantages of Metallic Mirrors |
|---|---|
| Reflects light evenly over many colors | Some light is lost by absorption |
| Works at many angles and polarizations | Can be damaged by strong light |
| Easy and cheap to make | Heat can change the mirror shape |
| Good for short light pulses | Reflects less than perfect (about 98% for silver) |
| Works well for long infrared light | Dielectric mirrors can absorb at long wavelengths |
Silver reflects the most but needs to be protected.
Gold resists rust and reflects infrared best.
Metal coatings are easy to make and reflect light evenly.
They can lose some light and may not last long in harsh places.
Tip: Think about where you will use the mirror and what kind of light you need. Each metal has its own good and bad points for optical coatings.
Dielectric coatings use thin layers of special materials. These layers help control how light bounces off a mirror. Engineers stack the layers to make mirrors that reflect almost all light at certain colors. These mirrors show bright and clear images. They work best for lasers, telescopes, and science tools that need strong reflection.
Dielectric coatings can reflect up to 99.999% of light at some angles and colors. This is better than what metallic coatings can do in many systems. These coatings also help the mirror not give off much heat. Many scientists pick dielectric coating mirrors because they work well in labs.
Manufacturers make dielectric coatings to last longer than old metallic coatings. Some dielectric mirrors use ar coatings to cut down glare and make images sharper. Anti-reflective coatings help make pictures clearer and stop stray light. Engineers use ar coatings in devices that need clear results.
Dielectric coatings can block unwanted light and help with anti-reflective needs. These coatings are good for places where mirrors must be strong and reliable. Many ar coatings meet military rules for being tough and lasting in harsh places. This means dielectric mirrors can handle wet air and very hot or cold weather.
Dielectric coatings help mirrors reflect more light and last longer. This makes them a top choice for many optical systems.
Dielectric coatings have many good points compared to metallic coatings. The table below shows how dielectric and metallic coatings are different.
| Aspect | Dielectric Coatings | Metallic Coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Up to 99.999% for specific angles and bands | Generally lower than dielectric |
| Wavelength Range | High reflectivity over a limited range | Reflectivity drops in blue/UV |
| Durability | Better durability compared to older metals | Less durable, especially over time |
| Performance in UV/Blue | Can perform poorly outside optimal range | Reflectivity also drops in these ranges |
Dielectric coatings reflect a lot of light for certain colors and angles. They usually last longer than metallic coatings. Many dielectric mirrors use ar coatings to work better. These ar coatings help cut glare and make things clearer. Dielectric coatings also help keep mirrors cool.
But dielectric coatings have some bad points. They may not work well outside their special color range. Some dielectric mirrors lose reflection in blue or ultraviolet light. These coatings may not be as tough as metallic ones if the mirror gets hit or scratched.
Weather and other things can change how long dielectric coatings last. Many ar coatings are made to stay strong in very hot or wet places. These coatings meet military rules for being reliable. Dielectric mirrors often keep working even when the weather changes fast.
ECI’s low loss dielectric mirror coatings work well in tough weather.
Many dielectric coatings meet military rules for being strong and lasting.
Dielectric mirrors often last longer than metallic mirrors in hard places.
Dielectric coatings help keep mirrors cool and cut down glare. Many ar coatings make mirrors better for science and factories. People pick dielectric mirrors when they need strong reflection, toughness, and cool surfaces. These coatings are good for places where mirrors must stay clear and work well.
Tip: Dielectric coatings give mirrors strong reflection and last a long time, but users should check if the coating works for their color needs.
Hybrid coatings mix metallic and dielectric layers together. Engineers make these coatings to reflect more light and last longer. They use metals like silver or aluminum first. Then, they put dielectric layers on top of the metal. These layers keep the metal safe from rust and scratches. Hybrid coatings work well in places with wet air or changing weather. Scientists use them in telescopes, cameras, and lasers. You can clean these coatings with alcohol or acetone. This helps the mirrors stay clear. Hybrid coatings do not tarnish fast and keep their shine longer than plain metal coatings.
Hybrid coatings often have anti-reflective layers too. These layers help stop glare and make images look better. Special thin films in hybrid coatings make light bounce in special ways. Hybrid coatings can reflect many colors and work at many angles. Many labs and factories use hybrid coatings for better results.
Enhanced coatings make hybrid coatings work even better. Protected silver coatings have a dielectric layer on top. This layer keeps the silver from rusting. It also lets you clean the mirror safely. Silver reflects lots of visible and infrared light. Enhanced coatings help in systems that need to reflect many kinds of light. The extra layer stops tarnishing, especially in dry places. Enhanced hybrid coatings also use anti-reflective layers to cut glare and make images sharper.
Hybrid coatings with these features reflect light well and help keep things cool. The table below shows how hybrid coatings compare to regular coatings.
| Metric | Value Range | Median Value |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Solar Reflectivity | Up to 97% | 97% |
| Surface Emissivity | Up to 0.97 | 0.97 |
| Surface Temperature Reduction | 2 to 35 °C | 9.6 °C |
| Sub-ambient Cooling | 2 to 13 °C | 5 °C |
| Cooling Power | 35 to 135 W/m² | 77 W/m² |
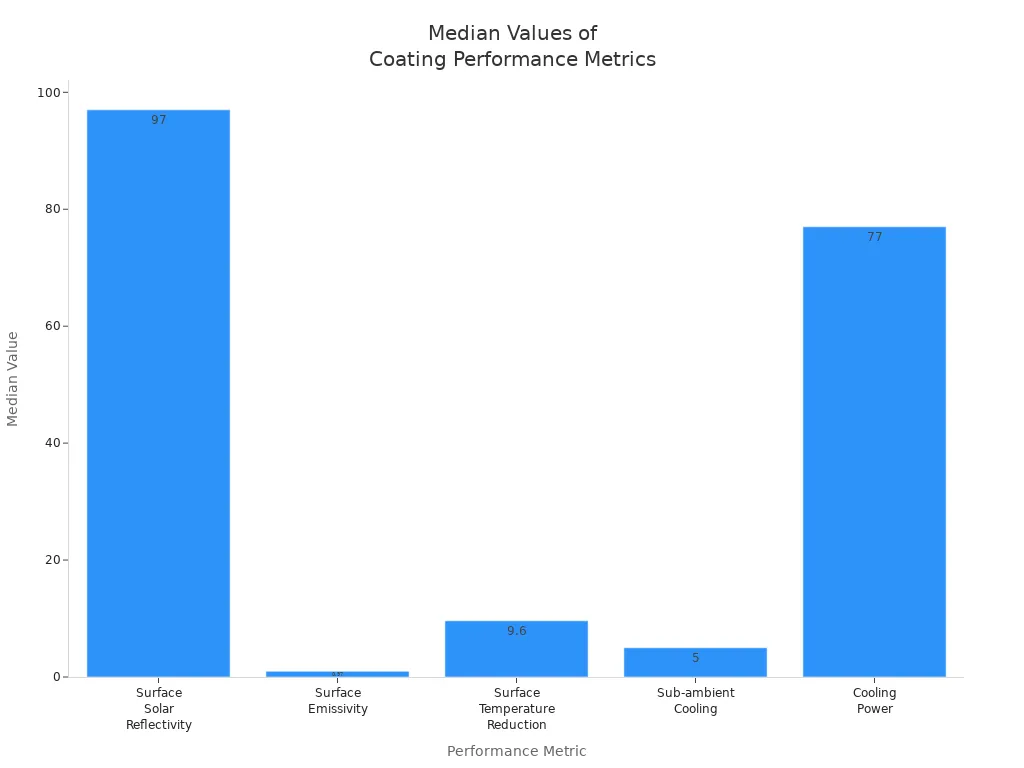
Hybrid coatings have many good points. They reflect a lot of light and protect mirrors well. They are easy to clean and last longer than plain metal coatings. Anti-reflective layers help cut glare and make things clearer. Hybrid coatings work well in tough places and keep mirrors working for years.
But hybrid coatings can cost more than simple metal coatings. If they are not made right, they may not reflect better. Making hybrid coatings can need special care. Some hybrid coatings can still get a little rusty after a long time.
Hybrid coatings give mirrors strong protection and high performance. They help optical mirror coatings last longer and work better in many systems.
Optical coatings help mirrors work better in different ways. Metallic coatings like silver and aluminum reflect most visible light. Silver reflects the most, up to 95%. Gold is best for infrared light. Dielectric coatings can reflect almost all light at some colors and angles. Some dielectric mirrors reflect up to 99.999%. Hybrid coatings mix metals and dielectric layers. These coatings give strong reflection and extra protection. Many scientists use anti-reflective layers to make images sharper. Anti-reflective coatings help mirrors show clearer pictures in telescopes and cameras.
| Coating Type | Reflectivity (Visible) | Reflectivity (Infrared) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | ~90% | Good | General optics |
| Silver | ~95% | Good | High-quality imaging |
| Gold | ~98% (IR) | Excellent | Infrared, harsh places |
| Dielectric | Up to 99.999% | Limited | Lasers, precision tools |
| Hybrid | 95-98% | Good | Outdoor, tough places |
Dielectric coatings reflect the most light for special colors. Metallic coatings work better for many colors.
Durability is important for mirrors in hard places. Aluminum can handle some rust but wears out in wet air. Silver needs protection from water and sulfur. Gold lasts the longest and does not rust. Dielectric coatings stay strong in labs and meet tough rules. Hybrid coatings use anti-reflective layers and protect metals from damage. Many hybrid mirrors last longer than plain metal mirrors. Anti-reflective coatings help mirrors resist scratches and work in changing weather.
Aluminum: Lasts 1-2 years in labs or outside.
Silver: Needs protection, lasts 1-2 years.
Gold: Does not rust, lasts longest.
Dielectric: Handles heat, water, and scratches.
Hybrid: Gives protection and lasts a long time.
Cost is important when picking a coating. Aluminum is the cheapest and works for many jobs. Silver costs more because it reflects better. Gold is the most expensive and used for special needs. Dielectric coatings cost more to make but last longer. Hybrid coatings cost the most because they use metals and special layers. Anti-reflective coatings add to the price but help mirrors work better.
| Coating Type | Cost Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Low | Good for basic needs |
| Silver | Medium | Needs protection |
| Gold | High | Used for infrared and space |
| Dielectric | Medium-High | Lasts longer, more precise |
| Hybrid | High | Best protection, longest life |
People should think about how well the coating works, how long it lasts, and the cost. Anti-reflective layers can help mirrors work much better.
Picking the best optical mirror coating depends on how you use the mirror. Scientists and engineers think about a few key things before they decide. They want coatings that help mirrors reflect light well and last longer. For important science tools, these things matter most:
Optical performance: The coating should help the mirror reflect more light and let some light pass through.
Durability: The coating should not scratch or wear out easily.
Environmental resistance: The mirror should work in wet or very hot and cold places.
Cost: The coating should not cost more than the project allows.
People often pick anti-reflective coatings for tools that need clear pictures and less glare. These coatings help telescopes, cameras, and microscopes show sharp images. Engineers also use anti-reflective layers in laser systems to make them work better.
The place where the mirror is used is very important when picking a coating. Some mirrors are in places with strong chemicals, bright UV light, or fast temperature changes. Coatings help keep mirrors safe in these hard places. For example, mirrors in airplanes need coatings that can handle very hot and cold weather and strong light. Military tools need coatings that stay strong in rough places. Science labs use coatings that do not get hurt by chemicals or water.
The aerospace industry uses coatings for very hot and cold places and strong light.
Military tools need coatings that work in tough places.
Research labs use coatings that do not get damaged by chemicals.
Engineers also look at what the mirror is made of and the angle of the light. These things help them pick the best anti-reflective coating for each job.
How much a coating costs is important when choosing one. Aluminum coatings are cheap and good for simple jobs. Silver and gold coatings cost more but work better for special uses. Dielectric and hybrid coatings cost the most because they last longer and protect better. Anti-reflective coatings make the price go up but help mirrors work better in many tools.
| Coating Type | Cost Level | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Low | General optics |
| Silver | Medium | High-quality imaging |
| Gold | High | Infrared, harsh places |
| Dielectric | Medium-High | Precision instruments |
| Hybrid | High | Outdoor, tough places |
Tip: People should pick a coating that fits their needs, where they will use it, and how much they can spend. Anti-reflective coatings often give the clearest images and best protection.
Metallic coatings reflect light well and are cheaper. But they might not last long in harsh places. Dielectric coatings reflect some colors very well and are hard to damage. Hybrid coatings protect mirrors and work great, but they cost more.
Engineers need to pick the right coating for each job. An anti-reflective coating helps stop glare. These layers make images look better and last longer. People should think about what they need, where they use it, and the price before choosing.
Dielectric coatings have layers made from special materials. These layers help reflect more light at certain colors. Metallic coatings use metals like silver or aluminum. Dielectric coatings last longer and work better for lasers.
Dielectric coatings are best when you need strong reflection and long life.
Most coated mirrors need to be cleaned gently. Alcohol or acetone is safe for hybrid coatings. Regular glass cleaner can hurt some coatings. Always read the manufacturer’s instructions before cleaning.
Use soft cloths.
Do not use strong chemicals.
Gold is rare and costs a lot. Gold coatings reflect infrared light really well. Scientists use gold for special tools like space telescopes. Aluminum and silver are cheaper and used for many jobs.
| Coating | Cost | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Gold | High | Infrared, space |
| Silver | Medium | Imaging |
| Aluminum | Low | General optics |
Most coatings last about one or two years in labs or outside. Gold coatings last longer because gold does not rust. Dielectric and hybrid coatings often last longer than metal coatings.
How long a coating lasts depends on where and how people use the mirror.