close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-07 Origin: Site
CNC glass machining uses smart computer tools to cut High-Transmittance Optical Glass. This process makes detailed patterns and shapes. These are needed for special optical designs. The machines work fast and make exact changes. This helps keep the glass clear and working well. Experts also use laser cutting and diamond wire ways. These help with fragile glass materials.
CNC technology cuts down on waste and makes sure each piece is made right. This helps create better optical products.
CNC machining makes very accurate cuts in high-transmittance optical glass. It can cut with an error of only ±0.01mm. This helps lower mistakes in optical parts.
High-transmittance optical glass is needed for clear pictures in many uses. It is used in medical imaging and aerospace. Its special features help optical devices work better.
CNC technology helps use less material and keeps quality the same in every batch. This makes optical products better and lowers how much it costs to make them.
Other ways to cut glass, like laser and diamond wire cutting, have their own good points. Laser cutting works best for thin glass. Diamond wire cutting is better for thick glass and for very exact optics.
Checking quality often and handling glass carefully during cutting keeps it clear and strong. This makes sure the glass meets high standards for how well it works.

Image Source: pexels
High-transmittance optical glass lets light pass through easily. It loses very little light. This makes it useful for many devices. The glass is very clear. It does not react much with chemicals. It is easy to shape and cut. CNC machines help make the glass into the right shapes.
High-transmittance optical glass helps people see clear images. It also helps measure things accurately in many areas.
The table below lists types of high-transmittance optical glass. It also shows what they are used for:
| Type of Glass | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| HT and HTultra | Very high-quality, optimum transmittance, improved color contribution | Prisms for 3D cameras, high-end projection systems, binoculars |
| High Homogeneity Glass | Extremely narrow variation in refractive index, superior quality | High-power lasers, wavefront sensitive metrology, satellite technology, astronomical applications |
| i-Line Glass | High refractive index homogeneity, high UV transmittance at 365 nm | Specialized optical applications requiring UV transmittance |
Physical and optical properties are important for how the glass works. These include:
Density: Goes from 2.39 g/cm³ to 6.19 g/cm³.
Thermal Expansion Coefficient: Usually between 7.00 to 9.00 x 10^–6/°C.
High transparency: Lets light go through well.
Chemical stability: Does not change much in different places.
Good processing performance: Makes CNC cutting easy and exact.
Many industries use high-transmittance optical glass. Here are some examples:
Screens for electronics
Medical imaging machines
Science tools and telescopes
Car and airplane sensors
Security and safety cameras
High-transmittance optical glass is very important for special optical designs. Engineers pick this glass for clear pictures and good measurements. The table below shows how different jobs use this glass:
| Application Area | Benefit of High-Transmittance Optical Glass |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Keeps light loss and distortion very low for exact optics. |
| Medicine | Gives clear views for medical tests and pictures. |
| Industrial Metrology | Makes measurements more accurate with good glass parts. |
| Consumer Cameras | Helps cameras take sharp and detailed photos. |
| Digital Projectors | Shows very clear images with lots of light passing through. |
High-transmittance optical glass helps designers control light exactly. It helps make sharp images. This glass is used to build new and better devices in many areas.
CNC machining lets engineers cut optical glass very precisely. Machines can make cuts as close as ±0.01mm. This accuracy helps stop mistakes in lenses and prisms. Computer programs make sure each piece matches the design. Operators use computers to keep every cut the same. Quality checks watch the process and help keep results repeatable.
Computer programs help make every batch the same. Quality checks make sure each batch is repeatable.
The table below compares CNC machining to older ways for high-transmittance optical glass:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision and Accuracy | CNC machines cut glass with very small errors. This is good for detailed designs and tight spaces. |
| Consistency | CNC machines make the same cuts over and over. This keeps all pieces looking the same. |
| Efficiency | CNC glass cutting is faster than cutting by hand. This saves time and makes more pieces. |
| Versatility | CNC machines work with many glass types and thicknesses. They can make hard shapes easily. |
| Safety | CNC keeps people away from dangerous work. This lowers the chance of getting hurt. |
CNC machining can make hard shapes and curves. This helps designers make special optical parts. The process saves glass by using sheets wisely. It also lowers costs and makes work safer by using less manual labor.
High-transmittance optical glass needs careful cutting to stay good. CNC machining makes smooth surfaces with little roughness. These features help keep the glass flat and clear. Careful tests check how clear and pure the glass is. Haze and light passing through affect how the glass looks and works.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Light Transmission | How much light goes through the glass compared to what hits it. |
| Haze | How cloudy the glass is because of scattered light, shown as a percent. |
| Clarity | How see-through and clean the glass is, which affects how it looks. |
| Reflectivity | How much light bounces off the glass, which matters for how it works. |
CNC machining helps keep glass clear and clean. The process supports high light passing and low haze. Engineers use these rules to check finished glass. This makes sure the glass works for cameras, sensors, and science tools.
CNC machining removes glass quickly and well. The process uses smart controls to take away material fast and accurately. Things like laser pulse time, wavelength, speed, and energy change how well glass is removed. Burst-mode and line-shaped focus help make better cuts and lower heat.
Laser pulse time changes how energy is given.
Wavelength changes how much is absorbed and how well it works.
Speed helps remove glass faster.
Pulse energy changes how well and safely glass is cut.
Burst-mode helps cut better with less heat.
Line-shaped focus makes cuts smoother.
CNC machining makes glass flat and smooth. These features help glass work well in optical systems. The process is fast and keeps glass strong. Engineers pick CNC machining because it is quick, accurate, and makes good quality.

Image Source: pexels
Engineers begin by making designs in CAD software. They draw 2D shapes or build 3D models. These show the size and shape needed. The team checks the glass blank for any problems. They look for cracks or marks before cutting. Several inspection tools help them check the glass. The table below lists common ways to inspect glass:
| Inspection Technology | Description | Tools/Equipment Used |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Inspectors look for scratches or color changes. | Magnifying Glasses, Lighting |
| Optical Metrology Systems | Uses light to find surface problems very accurately. | Optical Sensors, Image Processing Software |
| Machine Vision Systems | Cameras and software spot defects by themselves. | Cameras, Lighting Systems, Software |
| Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) | Measures the shape to find uneven spots. | CMM Machine, Measurement Software |
| Ultrasonic Testing | Sends sound waves to find hidden cracks. | Ultrasonic Transducer, Couplant |
| 3D Scanning | Makes a map to check how rough the glass is. | 3D Scanner, Software |
After checking, engineers make sure the glass is strong and clear. This step helps stop problems during cnc machining.
Operators get the cnc machine ready with care. They hold the glass blank tightly in place. The right cutting tools are put in the machine. The team sets things like spindle speed and feed rate. Calibration must be perfect because small mistakes matter. Computer programs guide the cutting head. These programs use the CAD data and follow the design. Good setup helps the machine work fast and meet strict rules for optical glass.
Tip: Careful setup and calibration help avoid errors and keep glass quality high.
During cutting, the cnc controller moves the cutting head. It follows the programmed path. Engineers watch the process to keep it steady. They listen to the sound while cutting. Strange sounds can mean something is wrong. The team checks tool wear often. Sharp tools help make clean cuts. They also inspect the glass during cutting. Keeping settings safe helps avoid problems.
Listening to cutting sounds helps find issues early.
Stable cutting keeps results the same each time.
Checking tool wear keeps cuts clean.
Watching the process checks if parts are made right.
Laser technology is often used with cnc machines. Lasers can cut glass very precisely. They help stop chipping. Engineers change laser settings like pulse time and wavelength. This controls how much glass is removed. Using cnc and lasers together helps make smooth surfaces and work quickly.
After cutting, the team polishes the glass to make it clear. They use waterproof sandpaper in steps. They start with rough sandpaper and move to smoother ones. Wet-sanding takes away marks from each step. Next, they use a cloth wheel and polishing paste. This makes the glass shiny again. Sometimes, flame polishing melts the surface a little. This gives the glass a glossy look. The last step is adding a hard anti-reflective coating. This protects the glass and makes it look better.
Quality control is very important. Engineers test each piece for size and optical properties. They use calipers and comparators to measure the glass. Careful testing helps find problems early. Checking and improving keeps standards high. Advanced methods help make sure every optical glass part is made well.
Note: Careful polishing and strict testing help keep the glass clear and meet all needs for optical glass.
Laser cutting uses strong light to shape optical glass. Engineers pick this way for thin glass and tricky shapes. The laser melts or turns the glass into gas along a set path. This makes smooth edges and tiny details. Operators change the laser’s pulse time and energy to control the cut. Laser cutting is good for light optics because it does not touch the glass.
Laser cutting has many good points:
It makes exact cuts for hard designs.
It works fast for making lots of pieces.
It puts little stress on the glass.
But laser cutting can make tiny cracks and hot spots. These problems can lower the glass quality if not watched closely. The cut width is very small, usually from 0.05 to 0.1mm. Engineers use laser cutting for thin glass and shapes that need fine detail.
Diamond wire cutting uses a thin wire with diamond bits. The wire moves fast and cuts thick optical glass. This way can reach a tolerance of ±0.02mm. That is important for aerospace, medical imaging, and making chips. The process makes a very smooth surface, often less than 0.2µm Ra. Engineers like diamond wire cutting for thick glass and exact optics.
The table below shows how diamond wire saws compare to other ways:
| Parameter | Diamond Wire Saw | Diamond Blade | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 0.1–0.3µm | 0.5–1.0µm | 0.5–2.0µm |
| Subsurface Cracks | Almost none | Moderate | Possible micro-fractures |
| Kerf Width | 0.15–0.3mm | 0.4–0.6mm | 0.05–0.1mm (but with HAZ) |
| Thermal Impact | None | Low | High (risk of stress birefringence) |
| Best For | Thick optical glass (>3mm), precision optics | Rough cutting, thick blocks | Thin glass, complex shapes |
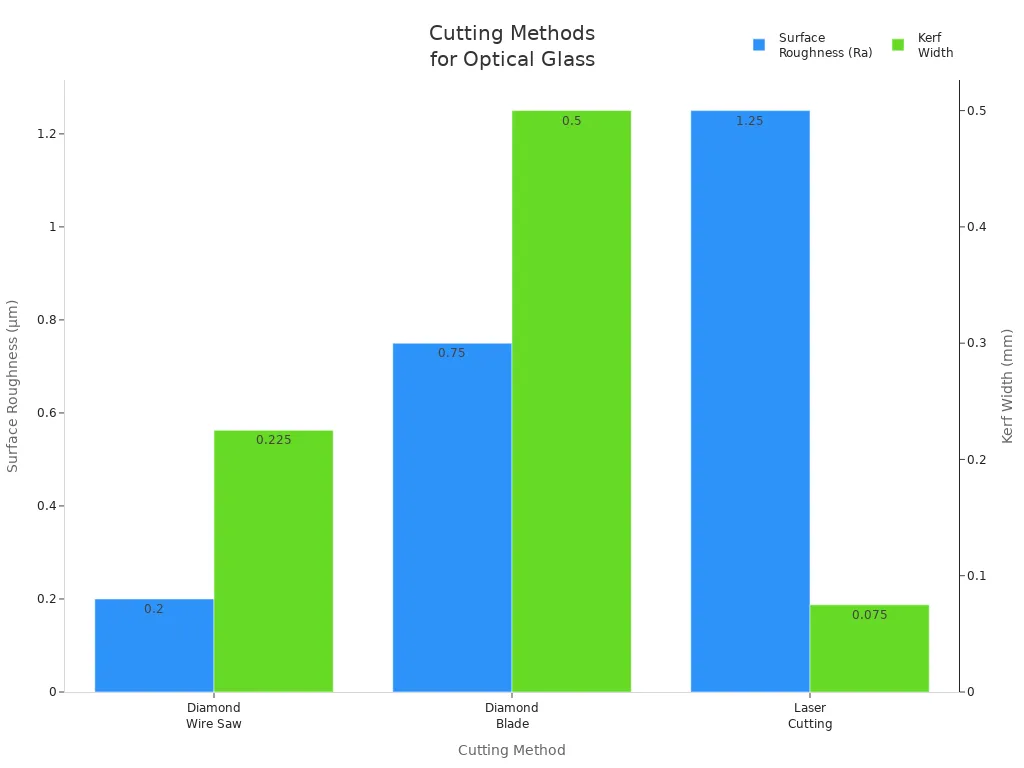
Diamond wire cutting makes almost no cracks under the surface. The process keeps the glass strong and clear. Engineers use this way for expensive optical parts. It helps make light optics and tricky shapes with high accuracy.
Tip: Diamond wire cutting is best for thick glass and parts that need a smooth finish.
Micro-cracks can make optical glass weaker and less clear. Engineers use different ways to stop these tiny cracks during CNC cutting. They blow cool air at the spot where the glass is cut. This stops the glass from getting too hot. Special lubricants help the cutting tool move easily. The room stays at a set temperature for careful work. Cooling the glass slowly stops sudden changes and stress inside.
Stress-relieving steps are very important. Technicians heat the glass almost to its change point, then cool it slowly. They leave extra material and let the glass rest before final cuts. Machining in steps and checking between each step finds problems early. Mapping the temperature in the room helps control how the glass grows or shrinks.
High-transmittance optical glass needs to stay clear after cutting. Clean tools and rooms help keep dirt away. Engineers polish the glass to remove rough spots. They add anti-reflective coatings to let more light through. Careful handling stops fingerprints and dust from making the glass cloudy. Regular checks look for haze or fog. These steps help the glass work well in cameras, sensors, and science tools.
Dimensional accuracy is important for optical glass parts. Engineers use special measuring tools to check tiny details. Strict quality checks happen all through making the parts. The table below lists ways to measure:
| Measurement Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| CMM | Checks if the part size is correct. |
| Interferometers | Measures how smooth and flat the surface is. |
| Optical Comparators | Compares part sizes to the right standards. |
Workers check each part after cutting and polishing. They match the results to the design plans. This makes sure every piece fits and works right.
Careful watching and smart tools help keep every optical glass part correct and dependable.
CNC cutting of optical glass can cause chipping and heat damage. Chipping makes the edges rough and weak. Heat damage can change the glass and make it worse. Engineers use different wires to help with these problems. Endless diamond wire works much better than reciprocating wire.
| Metric | Reciprocating Wire | Endless Diamond Wire | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Chip Depth | 120 μm | 22 μm | ↓ 81.7% |
| Edge Break Rate | 12% | 1.2% | ↓ 90% |
| Rework Time per Piece | 8 min | 2 min | ↓ 75% |
| Ra (Edge Surface) | 0.38 μm | 0.12 μm | Improved polishability |
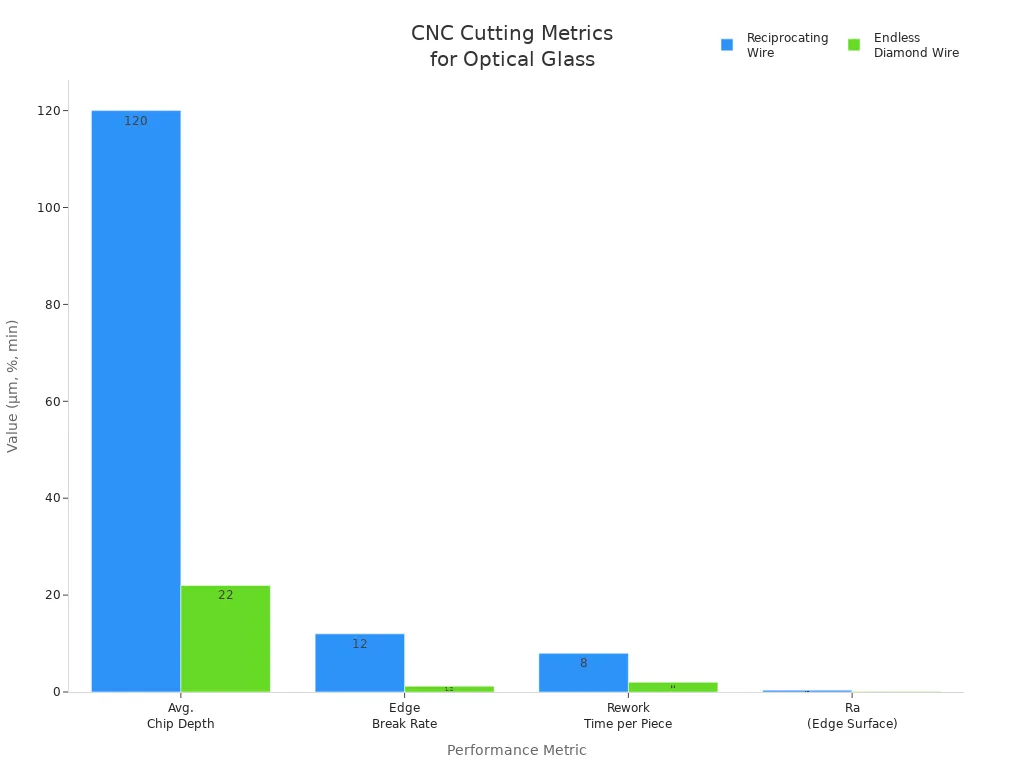
Engineers use many ways to stop heat damage:
Cooling helps keep the glass safe. Compressed air works for light cuts. Mist cooling with water-based coolants helps with deep cuts. Flood cooling is not used because it can shock the glass.
Picking the right tool is important. Sharp carbide tools with smooth surfaces and good angles cut better. Special drill bits with steep angles help stop chipping.
Speed and feed rates must be set right. Cutting speeds from 500 to 1000 ft/min work well. Many light passes keep heat low.
Good planning and the right tools help keep the glass strong and clear.
Optical glass can be different in each batch. These changes affect how the glass is cut and polished. Engineers test every batch before starting. They check density, clarity, and chemical makeup. If the glass acts differently, they change machine settings. Sometimes, they change the cutting speed or use new tools. Regular checks during cutting help find problems early.
Engineers use sensors to watch the glass while cutting.
They write down data and compare it to old batches.
If they see changes, they change the process to keep quality high.
Smart checks and quick changes help keep every piece of optical glass at top quality.
CNC glass machining helps engineers make strong, clear glass. Other advanced cutting methods also help with this job. These ways use careful steps to keep the glass good. Precision and high ablation efficiency help with custom optical designs. Many industries use these solutions for better results.
CNC and other methods give more options for future optical manufacturing.
High-transmittance optical glass helps engineers make lenses and mirrors. These parts let more light pass through in optics. Scientists use them in telescopes and cameras. They also use them in microscopes to see clear pictures.
CNC cutting makes surfaces smooth and edges sharp. This helps optics work better. Engineers use CNC machines for accuracy. Good quality means less light lost and clearer images.
Diamond wire cutting makes thick optical glass smooth. This way lowers cracks and keeps optics strong. Engineers use it for exact optics in medical tools. They also use it in aerospace and science equipment.
Technicians use special tools to measure size and clarity. They check if optics match design plans. Tests look at light passing through, haze, and flatness. Good results show the optics will work well.
Laser cutting can make tiny cracks or hot spots in optics. Engineers watch the process closely. They change laser settings to protect the glass. Careful control keeps optics clear and strong.