close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-07 Origin: Site
CNC Cutting Precision standards help makers build optical glass parts with exact sizes and trusted rules. Many businesses need parts with tolerances between ±5 and ±10 microns for good quality. New machines can make parts with even better accuracy. Precision is important because optical glass must work well in telescopes, lasers, and microscopes. Each use needs smooth surfaces and the right shapes. Band Optics uses advanced CNC glass machining to follow strict rules and give trusted solutions for important needs.
CNC cutting precision standards help optical glass parts fit exact sizes and meet quality needs. This is very important for medicine and technology uses.
Very small tolerances of ±5 to ±10 microns are needed for good optical glass. Even tiny mistakes can cause big problems in how the glass works.
Picking a certified provider like Band Optics means they follow strict rules. This makes sure the optical glass is safe and works well for many industries.
Regular checks during CNC machining find and fix problems early. This keeps the optical glass at a high standard.
Always improving CNC machining helps make parts more accurate and efficient. This gives better products and less waste.
CNC cutting precision means how well a machine can shape optical glass to match exact sizes. Engineers use CNC machines to make parts with very small differences. These machines follow computer instructions to cut, grind, and polish glass. Every step must meet strict rules so the finished part works right.
The units and settings for cnc cutting precision help experts check if a part is made correctly. The table below lists some common settings used in the process:
| Parameter Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Mechanical | Flange diameter, center thickness (CT), radius of curvature, clear aperture (CA) |
| Optical | Focal length, surface form (Power/Irregularity), material imperfections, centering deviation |
| Tolerances | Change based on system needs, assembly method, and materials used |
CNC cutting precision makes sure each part matches the plan. Technicians measure the diameter, thickness, and curve. They also check the optical features, like focal length and surface smoothness. These checks help make sure the glass will work well when used.
Precision is very important in optics. Optical glass needs exact shapes and smooth surfaces to guide light the right way. In labs, scientists use high-precision lenses to look at tiny things. Doctors need precise optical glass for surgeries with lasers. Even a small mistake in the glass can cause problems, especially in medical work where accuracy matters a lot.
High-precision optical parts give better accuracy and tighter limits than regular parts. This level of cnc cutting precision is needed for devices that must work perfectly every time. Optical glass is made from pure materials with almost no impurities. This purity helps the glass stay clear and strong, making it good for tough jobs.
Tip: Precision in cnc cutting precision helps stop mistakes and keeps people safe in medical, science, and industrial work.
CNC cutting precision helps make strong and reliable optical glass. Engineers and technicians use advanced machines to meet the needed standards. They check every detail to make sure the glass will work in telescopes, microscopes, and laser systems.
Engineers use two main standards for cnc glass machining. These are ISO 10110 and MIL-O-13830A/B. They set rules for how optical glass parts should look and work. Designers and inspectors use these standards to check if glass meets the right needs.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| MIL-O-13830A/B | Commonly used for checking surface quality in optical glass machining. |
| ISO 10110 | A more detailed standard that helps designers and makes checking easier for inspectors. |
ISO 10110 uses math to measure defect size and how often they appear. This gives more exact results. MIL-O-13830A/B uses people to look for problems, so results can change. ISO 10110 lets parts have smaller defects, which is good for high-precision work. MIL-O-13830A/B is quicker and costs less but might miss tiny issues.
| Aspect | ISO 10110 | MIL-O-13830A/B |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Method | Uses numbers to check defects | Inspector looks at the part |
| Defect Specification | Allows smaller defects | Only finds bigger defects |
| Inspection Process | Less likely to have mistakes | Depends on who checks |
| Testing Time | Takes longer because of details | Faster but not as exact |
Note: ISO 10110-7 takes more time but gives better results. MIL-PRF-13830B is faster but might not find every problem.
Tolerances show how close a part is to the plan. In cnc glass machining, tolerances for thickness, flatness, and surface quality matter. High-precision jobs need tighter tolerances and better specs.
| Quality Level | Tolerance Range (mm) | Typical Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| General | +0.00/-0.10 | Used in consumer lenses and lights |
| Precision | +0.00/-0.05 | Used in microscope lenses and cameras |
| High Quality | +0.000/-0.010 | Used in lasers and telescopes |
| Quality Level | Tolerance Range (mm) |
|---|---|
| General | ±0.20 |
| Precision | ±0.050 |
| High Precision | ±0.010 |
| Flat Optics Specifications | Commercial Quality | Precision Quality | Laser Grade Quality | Measurement Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Figure Accuracy, PTV @ 633nm | 3 waves/25mm | 1 wave | λ/4 | λ/20 |
| Surface Roughness, Angstroms RMS | – | <5 | ❤️ | <2 |
| Cosmetic QUALITY, Scratch-Dig | – | 40-20 | 20-10 | 5-1 |
| Center Thickness Tolerance (mm) | ±0.2 | ±0.1 | ±0.025 | ±0.005mm |
| Parallelism | – | 3’ | 30" | <2" |
| Diameter Accuracy (mm) | ±0.2 | ±0.1 | ±0.025 | +0.0/-0.025 |
| Transmitted Wavefront | – | 1 wave | λ/4 | λ/20 |
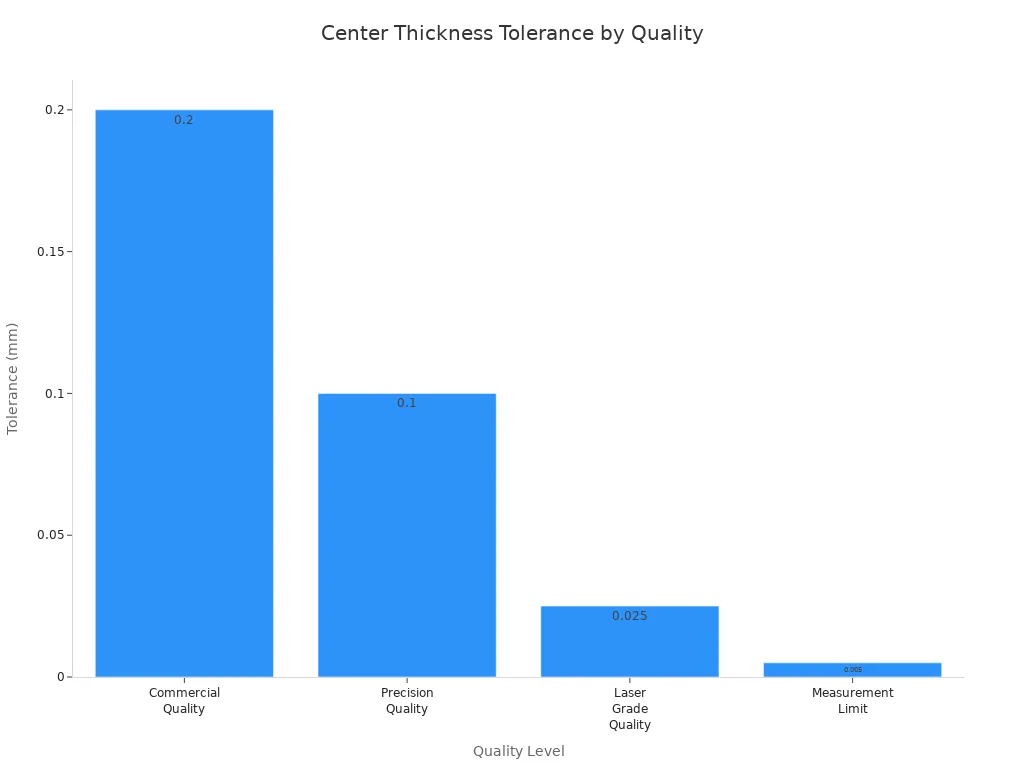
Tighter tolerances make optical glass cost more but work better. Commercial quality allows more changes from the plan. Precision and high precision need stricter rules for flatness and thickness. These are best for lasers and telescopes, where small mistakes can cause problems.
| Precision Level | Tolerances Impact on Cost | Allowable Deviations in Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial | Normal cost | More changes allowed |
| Precision | Costs 50% more | Needs tighter tolerances |
| High Precision | Costs another 50% more | Needs even stricter rules |
Band Optics follows strict rules in cnc glass machining. They use ISO 10110 and MIL-O-13830A/B to set specs for each part. Band Optics also has ISO 9001:2015 certification, which shows they have a strong quality system.
| Certification/Process | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 Certified Quality Management System | A rule for quality systems to keep products and services good. |
| ITAR Registration | Follows rules for exporting defense items. |
Band Optics uses advanced ways to meet specs for flatness, thickness, and surface quality. Their ISO 9001:2015 certification proves they care about quality. This helps Band Optics give good optical glass for medical, laser, chip, and space uses.
The company checks every part with the right rules and specs. Technicians measure flatness and thickness to make sure each piece is right. Band Optics uses new tools to check specs and keep quality high.
Tip: Picking a provider with ISO 9001:2015 certification, like Band Optics, helps make sure optical glass meets strict rules for flatness and other specs.
Surface quality is very important for optical glass. Engineers use different ways to check how smooth the glass is. Luminance measurements show how much light bounces off the glass. Luminance difference helps experts see changes in light reflection. Surface roughness indices use a laser microscope to show the glass texture.
Luminance measurements
Luminance difference
Surface roughness indices
Inspectors look for scratches, bubbles, or pits using scratch-dig specifications. They compare the scratch number to standard scratches with special lights. The dig number is found by dividing the dig’s size in microns by ten.
Scratch-dig specifications
Scratch number
Dig number
Industry standards say what surface quality is okay. MIL-PRF-13830B, ISO 10110, and ANSI/OEOSC OP1.002 set rules for surface roughness values.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| MIL-PRF-13830B | Military standard for optical glass |
| ISO 10110 | International standard for optical drawing specs |
| ANSI/OEOSC OP1.002 | American standard for optical surface quality |
Surface quality changes how well light goes through glass. Bad surface quality can scatter light and make things less clear. Good surface quality gives clear images and strong performance.
Surface flatness is a key thing in CNC cutting. Engineers use a machine with a ruby ball probe to measure flatness. Optical interferometry uses two light beams to make patterns and check flatness.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Coordinate Measuring Machine | Uses a contact ruby ball probe to sample points for surface flatness calculation. |
| Optical Interferometry | Creates interference patterns for precise surface flatness measurement. |
Flat surfaces help glass parts fit and work well in optical systems. Irregularity can scatter light and lower image quality. Even small flatness problems can cause big distortions. Surface flatness must meet strict standards to avoid issues in high-precision systems. Small irregularities may look fine but still hurt performance. Optics work at the nanometer scale, so flatness is very important.
Note: Scratches and pits can scatter light, lower transmission, and cause optical problems. In high-precision systems, even tiny flatness defects can make images worse.
Dimensional accuracy is very important for CNC-cut optical glass. Milling takes away glass to make exact shapes. Drilling makes holes of different sizes. Boring makes holes bigger for better finish and tolerance. Engraving adds complex designs. Grinding and polishing make the surface smoother and flatter. Water jet cutting uses strong water to cut glass with little waste. Edge grinding makes edges smooth and safe.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Milling | Removes glass to create features with high precision. |
| Drilling | Creates holes of various diameters. |
| Boring | Enlarges holes to precise dimensions. |
| Engraving | Adds complex designs to the surface. |
| Grinding | Improves surface quality and prepares for further processing. |
| Water jet cutting | Cuts glass with high-pressure water, reducing waste and stress. |
| Polishing and grinding | Enhances surface flatness and clarity for optical uses. |
| Edge grinding | Smooths edges for safety and aesthetics. |
High-precision industries need tight tolerances for diameter, center thickness, and flatness. The table below shows common tolerances:
| Tolerance Class | Diameter Tolerance | Center Thickness Tolerance | Radius of Curvature Tolerance | Angular Tolerance | Bevel Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 100 μm | 200 μm | 0.2% | 6 arc min | 0.2 mm |
| Precision | 25 μm | 50 μm | 0.1% | 1 arc min | 0.1 mm |
| High Precision | 6 μm | 10 μm | 0.01% | 15 arc sec | 0.02 mm |
Dimensional accuracy makes sure each part matches the plan and fits well in optical systems. Good surface flatness and quality help glass parts work well and last longer.
Technicians start by looking at each piece of optical glass. They check if the glass is clear and thick enough. They also look for any flaws. Only glass that passes these checks moves on. Workers clean the glass to get rid of dust and oils. Cleaning helps stop scratches when machining. Getting the material ready is important for high precision in glass cnc machining.
Engineers use CAD software to design each part. They turn these designs into CNC programs. Operators set up the CNC machines with the right tools. They hold the glass in place using vacuum systems. The glass cnc machining process uses cutting, milling, drilling, and engraving. Machines follow set paths to shape the glass with tight tolerances. Sensors watch temperature and vibration during machining. Technicians check the surface finish and change settings to keep quality high.
Tip: Watching the process closely helps stop mistakes and keeps every part within the rules.
Quality control is very important in cnc machining. Inspectors measure diameter, thickness, and flatness for each part. They use special tools like coordinate measuring machines and optical interferometers. Testing happens at different steps. First article inspections check accuracy before making more parts. After machining, workers polish the glass to make it smoother. Final tests look for scratches, pits, and other problems. Reports are made for each step to show every part meets the needed standards.
| Inspection Step | Purpose | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| First Article | Check first part is accurate | CMM, calipers |
| In-Process | Watch quality during work | Sensors, microscopes |
| Final | Check surface finish | Interferometers, lights |
Band Optics uses advanced CNC machines for glass cnc machining. Their machines do precision grinding and polishing for great surface finish. The company makes custom lens solutions for different needs. They change focal length and aperture size as needed. Band Optics keeps strict quality control during glass cnc machining. Their team uses high-speed polishing and MRF polishing for better surface finish. These methods help Band Optics give reliable optical glass for medical, laser, chip, and space uses.
Band Optics uses skill, new technology, and strong testing to make optical glass that meets top standards.
Machine calibration is very important for CNC cutting precision. Operators must set up machines the right way. This keeps tolerances tight and parts accurate. Good calibration helps make detailed designs. It also stops damage to glass edges. Bad calibration can chip or break the glass. Each material needs special calibration settings. Glass needs softer settings than metal. Operators use best steps to keep machines working well:
Run a test program and check results with the plan.
Teach operators to use measuring tools for accuracy.
Calibrate dial indicators and laser systems often.
Fix and recalibrate machines after any crash.
Use mag bases and dial gauges to set tool offsets.
Tip: Checking calibration often helps keep quality high and stops mistakes.
Material properties change how CNC cutting works on optical glass. Each property affects how glass acts during machining. The table shows key properties and what they do:
| Property | Impact on CNC Cutting Precision and Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Keeps light loss low for clear and sharp images. |
| Refractive Index | Controls light bending for lens design and light paths. |
| Dispersion | Fixes color errors for better image and color quality. |
| Thermal Properties | Keeps glass working well when temperatures change. |
| Resistance to Environmental Factors | Makes glass stable and strong, so it needs less fixing. |
Operators pick glass types by these properties for each job.
Inspection methods help check CNC cutting precision. Operators use different ways to test quality:
Visual checks find scratches and dents fast.
Size checks use calipers to measure parts.
Coordinate checks give 3D measurements for hard shapes.
Surface roughness checks find wear risks.
Non-destructive tests find hidden problems without breaking glass.
Functional and pressure tests copy real-life use.
Operators also watch the cutting process closely. They measure sizes while cutting. They check cutting force and speed. Vibration sensors and roughness tools help find problems early.
Note: Careful inspection makes sure every optical glass part meets strict rules for performance and reliability.
Picking a CNC provider for optical glass takes careful thought. You need to look at their skills and machines. Providers with new technology can make parts very accurate. They also make surfaces smooth and clear. Good companies use many steps to shape and finish glass. These steps include cutting, edging, lapping, polishing, cleaning, checking, and packing. The table below explains each step:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Cutting | Uses mechanical scribetables and water jet for detailed shapes. |
| Edging | Smooths edges and corners with diamond grinding wheels for safety. |
| Lapping | Offers single-side and double-side lapping for custom needs. |
| Polishing | Achieves clear surfaces with double-side polishing and low defects. |
| Cleaning | Uses ultrasonic cleaning in a clean room to keep glass pure. |
| Inspection | Applies advanced inspection to ensure every part meets standards. |
| Packaging | Provides custom packaging to protect quality and cleanliness. |
Providers who know these steps can give reliable optical glass for many jobs.
Quality assurance helps make sure every glass part is made right. Top providers use many ways to keep quality high. They focus on making parts with tight limits and picking good materials. New manufacturing methods help parts stay the same. Strong testing finds problems early. Watching and improving the process keeps standards high. The table below lists important practices:
| Quality Assurance Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision in Manufacturing | Makes sure parts meet tight standards with little error. |
| Material Selection | Picks the best materials for strong and effective components. |
| Advanced Manufacturing Techniques | Uses new technology for better precision and consistency. |
| Rigorous Testing Procedures | Checks for defects to deliver only top-quality products. |
| Continuous Monitoring and Improvement | Reviews and improves processes to keep quality high. |
Providers with strong quality checks can make parts that work well in tough places.
Band Optics is a trusted CNC provider for optical glass. The company gives precise cutting and great surface quality. Their team can make parts with tight limits and hard shapes. Band Optics also makes special shapes for new optical systems. The table below shows their main strengths:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Cutting | Delivers accurate parts for top performance. |
| Surface Quality | Provides clear and functional surfaces for optical uses. |
| Consistency | Ensures uniform parts, reducing differences in performance. |
Band Optics uses new technology and strong quality checks for medical, laser, chip, and space industries. Their ISO 9001:2015 certification proves they care about quality and trust.
Tip: Picking a provider with skill and certifications, like Band Optics, helps make sure optical glass parts meet top standards.
Quality in CNC glass machining needs good inspection. Technicians check each part for the right size and shape. They use special tools to measure thickness and diameter. Surface finish is also checked with these tools. Regular checks help find mistakes early. Operators follow rules for every part. These rules show the tolerances and specs needed.
Inspection teams use advanced machines to see every detail. They calibrate CNC machines often to keep them working well. Real-time systems watch for problems as parts are made. Data from these systems helps workers fix issues fast. Here are the steps for ongoing inspection:
Set clear tolerances and specs for each part.
Calibrate CNC machines on a set schedule.
Use advanced tools to check size and surface.
Watch machining in real time and collect data.
Regular inspection keeps CNC glass machining accurate and safe. Teams find and fix problems before they hurt the final product.
Continuous improvement helps companies make better glass parts. Teams look for ways to save time and cut waste. They use new technology for more accurate cutting. Workers plan jobs carefully and keep machines in good shape. These steps help companies stay ahead.
The table below shows how continuous improvement helps quality:
| Initiative | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Better technology | Improves cutting accuracy and quality |
| Careful planning | Saves time and reduces mistakes |
| Regular maintenance | Keeps machines working at top performance |
| Advanced measurement | Ensures every part meets high standards |
| Efficient operations | Reduces costs and boosts productivity |
Technicians use many tools to check each part during machining. These tools help them make sure every part is good. Advanced CNC machines can cut glass into complex shapes with high precision. Continuous improvement makes sure every part meets strict rules and helps companies give top products.
Continuous improvement helps businesses stay strong. Teams work together to make processes better and keep quality high.
CNC cutting precision standards help engineers make good optical glass. These standards help optical glass work better in medicine, lasers, and space. Certified providers like band-optics use new machines to meet tough rules for optical glass. Quality control checks each optical glass part so it works well in optical systems. Learning about new optical glass standards helps companies give better products.
Picking band-optics means you get optical glass you can trust for any optical use.
Cnc means computer numerical control. Engineers use cnc machines to shape glass. These machines follow computer instructions. They cut, grind, and polish glass surfaces. Cnc technology helps make optical parts for many industries.
Tight tolerances help parts fit and work well. Small changes make surfaces meet strict rules. This accuracy is needed in medical and biotech devices. Good tolerances keep performance and safety high.
Glass cnc machining has many good points. Engineers make exact shapes and smooth surfaces. Cnc machines build complex optical parts with steady quality. This process helps biotech and medical device industries.
Scratch-dig specifications help inspectors check glass surfaces. These rules show how many scratches or digs are okay. Meeting these specs keeps surfaces clear and strong for optical parts.
Cnc machining makes optical parts with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances. These features help devices work safely and well. Engineers use cnc to make reliable parts for biotech and medical devices.